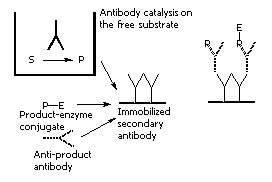
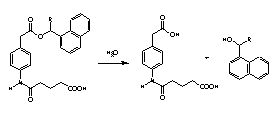
Screening of a large number of clones produced in a fusion is often the bottleneck in the isolation of catalytic antibodies. The usual approach requires two steps: clones are first selected for their high affinity to the antigen and then the good binders for their catalytic activity. Following this way, one looks for catalysis within a set of antibodies previoulsy selected for a different and not necessarily related property. To overcame this problem, Tawfik and Green developed the catELISA technique, which consist essentially in a non competitive ELISA test for the reaction product: plates are coated with a reagent conjugate which is transformed into product in the presence of a catalytic species.a
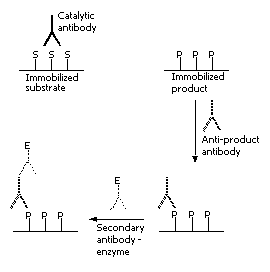
The non competitive catELISA